publications
2025
-
 Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural NetworksAleksei V. Belonovskii, Elizaveta I. Girshova, Erkki Lähderanta , and 1 more authorLaser & Photonics Reviews, Mar 2025
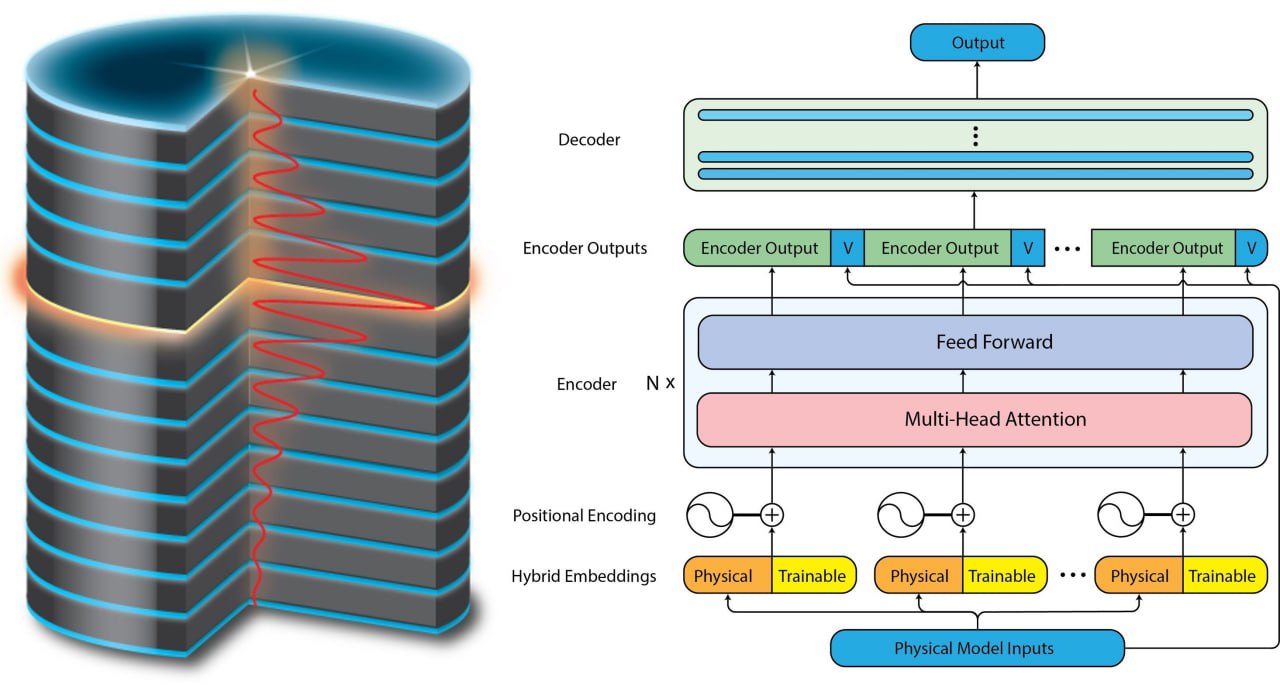
Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural NetworksAleksei V. Belonovskii, Elizaveta I. Girshova, Erkki Lähderanta , and 1 more authorLaser & Photonics Reviews, Mar 2025Abstract This study presents an innovative approach to predicting VCSEL emission characteristics using transformer neural networks. It is demonstrated how to modify the transformer neural network for applications in physics. The model achieved high accuracy in predicting parameters such as VCSEL’s eigenenergy, quality factor, and threshold material gain, based on the laser’s structure. This model trains faster and predicts more accurately compared to conventional neural networks. The transformer architecture also suitable for applications in other fields is proposed. A demo version is available for testing at https://abelonovskii.github.io/opto-transformer/.
@article{Belonovskii2025, title = {Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural Networks}, author = {Belonovskii, Aleksei V. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and L{\"a}hderanta, Erkki and Kaliteevski, Mikhail}, journal = {Laser \& Photonics Reviews}, year = {2025}, month = mar, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/lpor.202401636}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.1002/lpor.202401636}, }
2024
-
 Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural NetworksAleksei V. Belonovskii, Elizaveta I. Girshova, Erkki Lähderanta , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2407.06039, Jul 2024
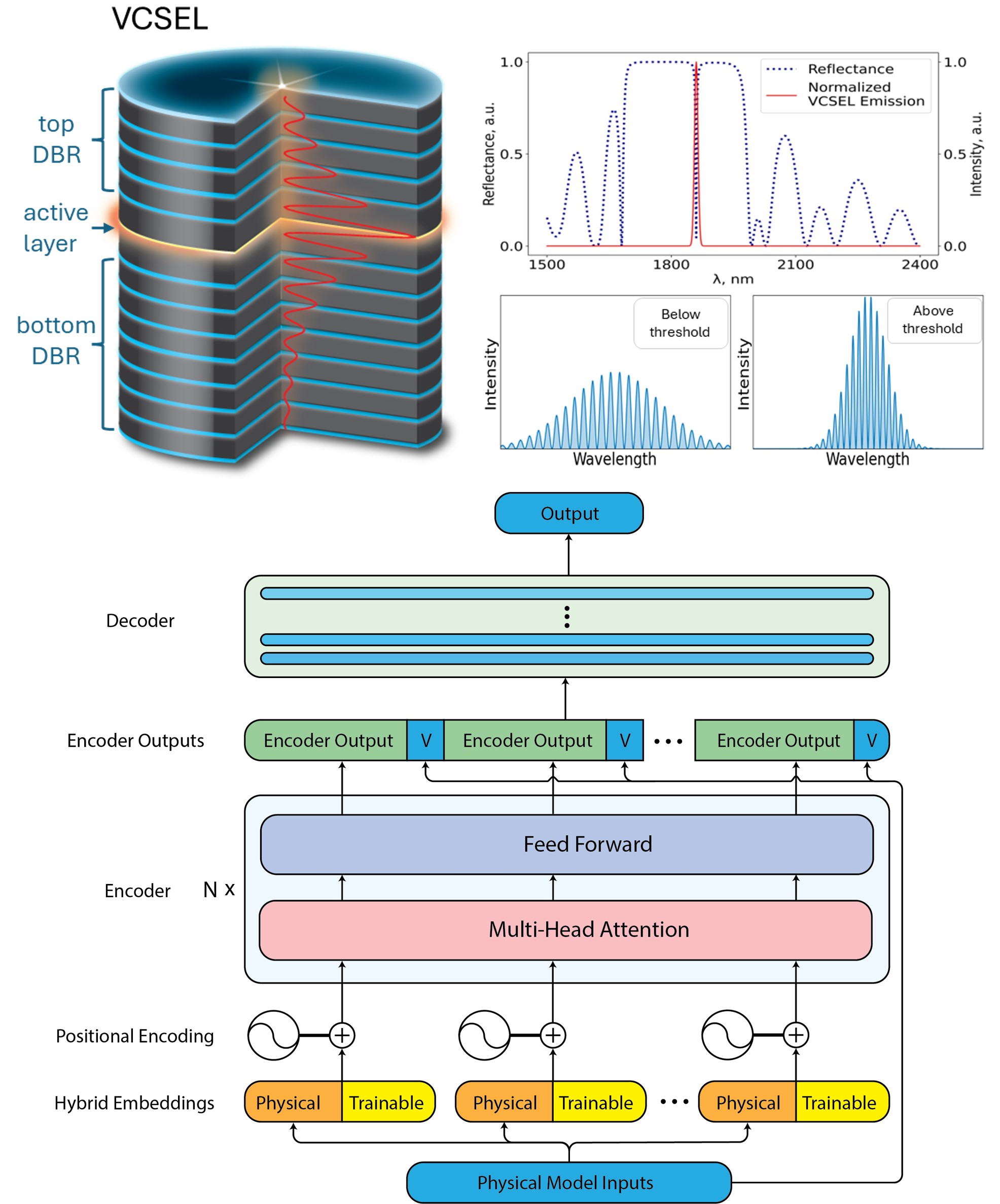
Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural NetworksAleksei V. Belonovskii, Elizaveta I. Girshova, Erkki Lähderanta , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2407.06039, Jul 2024This study presents an innovative approach to predicting VCSEL emission characteristics using transformer neural networks. We demonstrate how to modify the transformer neural network for applications in physics. Our model achieved high accuracy in predicting parameters such as VCSEL’s eigenenergy, quality factor, and threshold material gain, based on the laser’s structure. This model trains faster and predicts more accurately compared to traditional neural networks. The transformer architecture we propose is also suitable for applications in other fields. A demo version is available for testing at https://abelonovskii.github.io/opto-transformer
@article{Belonovskii2024, title = {Predicting VCSEL Emission Properties Using Transformer Neural Networks}, author = {Belonovskii, Aleksei V. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and L{\"a}hderanta, Erkki and Kaliteevski, Mikhail}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.06039}, year = {2024}, month = jul, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.06039}, dimensions = {true}, comments = {20 pages including appendix, 11 figures, 3 tables, intended for submission to a peer-reviewed journal}, keywords = {Disordered Systems and Neural Networks (cond-mat.dis-nn); Mesoscale and Nanoscale Physics (cond-mat.mes-hall)}, msc_classes = {68T01, 68T05, 78M50, 78A60, 81V80}, acm_classes = {I.2.0; I.2.6; J.2}, }
2023
-
 Strong Coupling of Exciton in Organic Material and Plasmonic Whispering Gallery Modes Localized on the Surface of Silver NanoparticlesA. V. Belonovskii, V. P. Evtikhiev, M. I. Mitrofanov , and 1 more authorJETP Letters, Jun 2023
Strong Coupling of Exciton in Organic Material and Plasmonic Whispering Gallery Modes Localized on the Surface of Silver NanoparticlesA. V. Belonovskii, V. P. Evtikhiev, M. I. Mitrofanov , and 1 more authorJETP Letters, Jun 2023The interaction of plasmonic whispering gallery modes on the surface of silver nanospheres with an exciton of the surrounding organic medium has been theoretically studied. DPAVBi (4,4’-bis[4-(di-ptolylamino) styryl]biphenyl) was selected as an organic material due to its high oscillator strength. The results show that for spheres of sufficiently large radii, several plasmon modes can be localized on their surface at once, which makes them possible for strong coupling with an exciton. The calculated spectra confirm that plasmon modes can effectively interact with excitons in the surrounding organic material, which leads to a significant change in both the absorption and emission characteristics of the system. These observations highlight the potential of such hybrid systems for a number of applications in optoelectronics and photonics, making them a promising platform for further research in this area.
@article{Belonovskii2023, title = {Strong Coupling of Exciton in Organic Material and Plasmonic Whispering Gallery Modes Localized on the Surface of Silver Nanoparticles}, volume = {118}, issn = {1090-6487}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S0021364023601562}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.1134/s0021364023601562}, number = {1}, journal = {JETP Letters}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Belonovskii, A. V. and Evtikhiev, V. P. and Mitrofanov, M. I. and Nikolaev, V. V.}, year = {2023}, month = jun, pages = {21–25}, } -
 Quasistationary Polariton States in MesocavitiesA. V. Belonovski, V. V. Nikolaev, and E. I. GirshovaJETP Letters, Jan 2023
Quasistationary Polariton States in MesocavitiesA. V. Belonovski, V. V. Nikolaev, and E. I. GirshovaJETP Letters, Jan 2023When the strength of light–matter interaction (the Rabi splitting) in mesocavities is comparable to the energy spacing between the cavity modes, an exciton mode is coupled simultaneously to a number of optical modes. It has recently been demonstrated that a nonmonotonic dependence of the population of polariton states in mesocavities on the pump intensity is possible. Here, it is shown that an additional quasistationary state may appear in the hysteresis region and the time spent by the system in this state depends on the pump intensity.
@article{Belonovski2023_2, title = {Quasistationary Polariton States in Mesocavities}, volume = {117}, issn = {1090-6487}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S0021364022602925}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.1134/s0021364022602925}, number = {2}, journal = {JETP Letters}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Belonovski, A. V. and Nikolaev, V. V. and Girshova, E. I.}, year = {2023}, month = jan, pages = {99–103}, }
2022
-
 Prospects for Using Organic and Metal−Polymer Materials in Optoacoustic Generators of UltrasoundE. I. Girshova, A. P. Mikitchuk, A. V. Belonovski , and 2 more authorsBulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics, Jul 2022
Prospects for Using Organic and Metal−Polymer Materials in Optoacoustic Generators of UltrasoundE. I. Girshova, A. P. Mikitchuk, A. V. Belonovski , and 2 more authorsBulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics, Jul 2022It is shown theoretically that introducing an additional organic layer with embedded metal nanoparticles into the design of an optoacoustic generator based on structures with a Tamm plasmon allows the efficiency of energy conversion at frequencies of modulation up to 100 MHz to be improved. Effective materials are selected for a device of the proposed design.
@article{Girshova2022, title = {Prospects for Using Organic and Metal−Polymer Materials in Optoacoustic Generators of Ultrasound}, volume = {86}, issn = {1934-9432}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.3103/S1062873822070140}, google_scholar_id = {3fE2CSJIrl8C}, doi = {10.3103/s1062873822070140}, number = {7}, journal = {Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics}, publisher = {Allerton Press}, author = {Girshova, E. I. and Mikitchuk, A. P. and Belonovski, A. V. and Morozov, K. M. and Kaliteevski, M. A.}, year = {2022}, month = jul, pages = {833–836}, } -
 Enhancement of the Basal-Plane Stacking Fault Emission in a GaN Planar Nanowire MicrocavityE. I. Girshova, G. Pozina, A. V. Belonovskii , and 6 more authorsJETP Letters, May 2022
Enhancement of the Basal-Plane Stacking Fault Emission in a GaN Planar Nanowire MicrocavityE. I. Girshova, G. Pozina, A. V. Belonovskii , and 6 more authorsJETP Letters, May 2022We study and compare optical microcavities formed by GaN planar nanowires. Nanostructures with structural defects such as stacking faults and without defects are considered. The behavior of an exciton localized in a stacking fault is considered. Different behavior of the photoluminescence intensity and the photoluminescence decay time is observed for the cases under consideration. Theoretical calculations show the localization of the field at the ends of the structure.
@article{Girshova2022_2, title = {Enhancement of the Basal-Plane Stacking Fault Emission in a GaN Planar Nanowire Microcavity}, volume = {115}, issn = {1090-6487}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S0021364022100605}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {8k81kl-MbHgC}, doi = {10.1134/s0021364022100605}, number = {10}, journal = {JETP Letters}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Girshova, E. I. and Pozina, G. and Belonovskii, A. V. and Mitrofanov, M. I. and Levitskii, I. V. and Voznyuk, G. V. and Evtikhiev, V. P. and Rodin, S. N. and Kaliteevski, M. A.}, year = {2022}, month = may, pages = {574–580}, } -
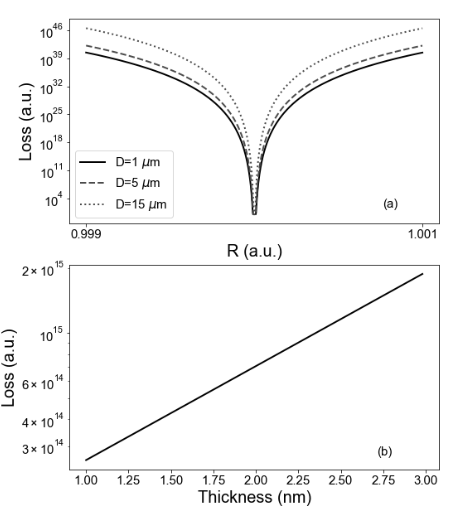 Genetic algorithm for optimizing Bragg and hybrid metal-dielectric reflectorsE.I. Girshova, A.V. Ogurtcov, A.V. Belonovski , and 2 more authorsComputer Optics, Aug 2022
Genetic algorithm for optimizing Bragg and hybrid metal-dielectric reflectorsE.I. Girshova, A.V. Ogurtcov, A.V. Belonovski , and 2 more authorsComputer Optics, Aug 2022Highly efficient reflectors are in demand in the rapidly developing optoelectronics. At the moment, distributed Bragg reflectors made of semiconductor materials are mainly used in this capacity. A lot of time and financial resources are spent on their production. Reducing the thickness of the reflector while maintaining its reflectivity would make these devices more affordable and extend their lifetime by reducing thermal noise. With the help of genetic optimization algorithms, the structures of multilayer semiconductor and combined metal-semiconductor reflectors were obtained, having a smaller thickness and equal optical characteristics than those of classical analogues. In particular, a 29% reduction in the thickness of the silicon/silica Bragg reflector was achieved without compromising performance.
@article{Girshova2022_3, title = {Genetic algorithm for optimizing Bragg and hybrid metal-dielectric reflectors}, volume = {46}, issn = {2412-6179}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.18287/2412-6179-CO-1128}, google_scholar_id = {MXK_kJrjxJIC}, doi = {10.18287/2412-6179-co-1128}, number = {4}, journal = {Computer Optics}, publisher = {Samara National Research University}, author = {Girshova, E.I. and Ogurtcov, A.V. and Belonovski, A.V. and Morozov, K.M. and Kaliteevski, M.A.}, year = {2022}, month = aug, } -
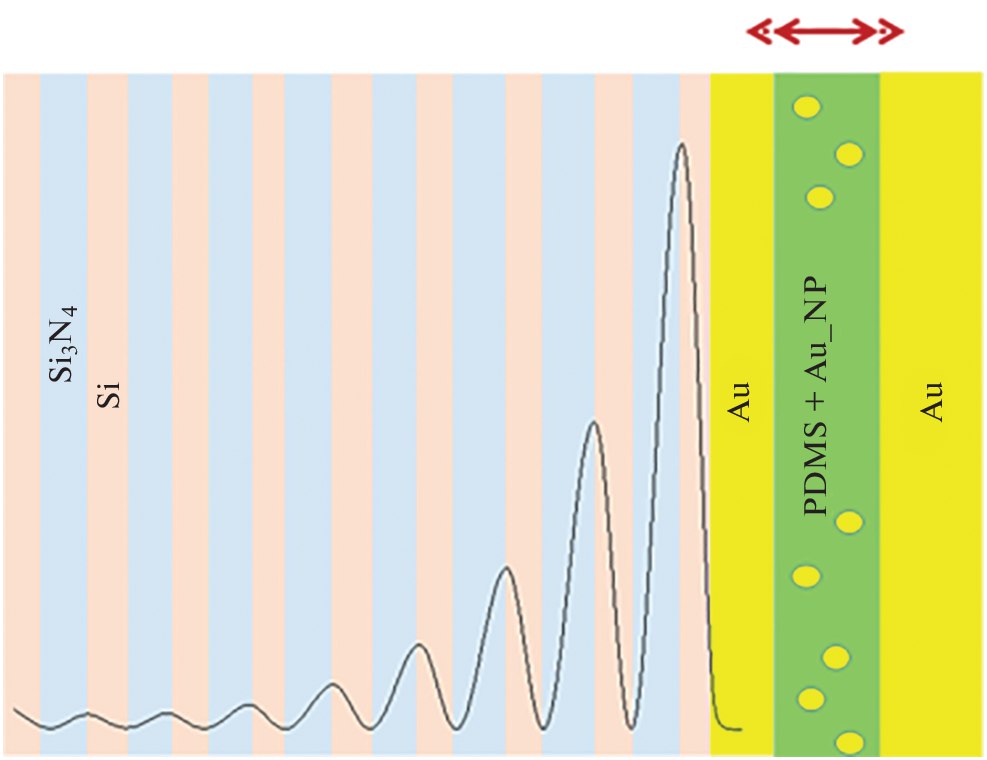
 Hybrid metal polymer as a potential active medium of an optoacoustic generatorGirshova E.I., Mikitchuk A.P., Belonovski A.V. , and 1 more authorTechnical Physics Letters, Aug 2022
Hybrid metal polymer as a potential active medium of an optoacoustic generatorGirshova E.I., Mikitchuk A.P., Belonovski A.V. , and 1 more authorTechnical Physics Letters, Aug 2022A hybrid material was studied, consisting of polydimethylsiloxane and silver nanoparticles distributed throughout its volume, its optical and thermodynamic characteristics were calculated for different volume fractions of silver content. It is theoretically shown that this material with a volume fraction of silver of about 30% can be used as an active medium for an optoacoustic transducer with an operating frequency range of about 10 MHz. Keywords: ultrasonic generator, polydimethylsiloxane, hybrid material
@article{GirshovaEI2022, title = {Hybrid metal polymer as a potential active medium of an optoacoustic generator}, volume = {48}, issn = {1726-7471}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.21883/TPL.2022.02.52842.18948}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.21883/tpl.2022.02.52842.18948}, number = {2}, journal = {Technical Physics Letters}, publisher = {Ioffe Institute Russian Academy of Sciences}, author = {E.I., Girshova and A.P., Mikitchuk and A.V., Belonovski and K.M., Morozov}, year = {2022}, pages = {32}, } -
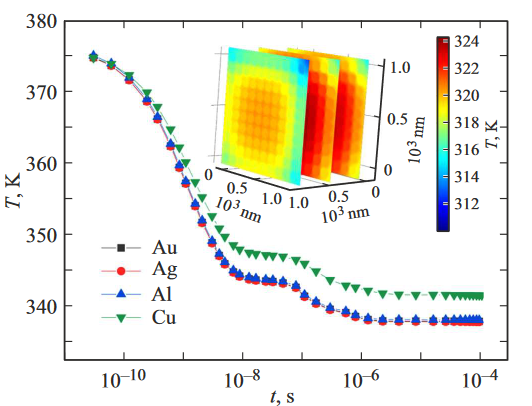 A hybrid metal polymer based on polymethyl methacrylate with embedded metal nanoparticlesGirshova E.I., Mikitchuk A.P., Belonovski A.V. , and 1 more authorSemiconductors, Mar 2022
A hybrid metal polymer based on polymethyl methacrylate with embedded metal nanoparticlesGirshova E.I., Mikitchuk A.P., Belonovski A.V. , and 1 more authorSemiconductors, Mar 2022A study was made of a hybrid metal-polymer material consisting of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and nanoparticles distributed throughout its volume, silver, gold, copper or aluminum. The effective permittivity and absorption cross section are calculated, and the processes of temperature relaxation are modeled. It has been shown that mixtures of PMMA with silver, copper, aluminum, or gold nanoparticles can be used as an active medium in optoacoustic ultrasound generators. Keywords: hybrid material, ultrasound generator, nanoparticle, polymethyl methacrylat.
@article{Girhova2022_4, title = {A hybrid metal polymer based on polymethyl methacrylate with embedded metal nanoparticles}, volume = {56}, url = {https://journals.ioffe.ru/articles/55160}, dimensions = {true}, number = {7}, journal = {Semiconductors}, author = {E.I., Girshova and A.P., Mikitchuk and A.V., Belonovski and K.M., Morozov}, pages = {458--460}, year = {2022}, month = mar, } -
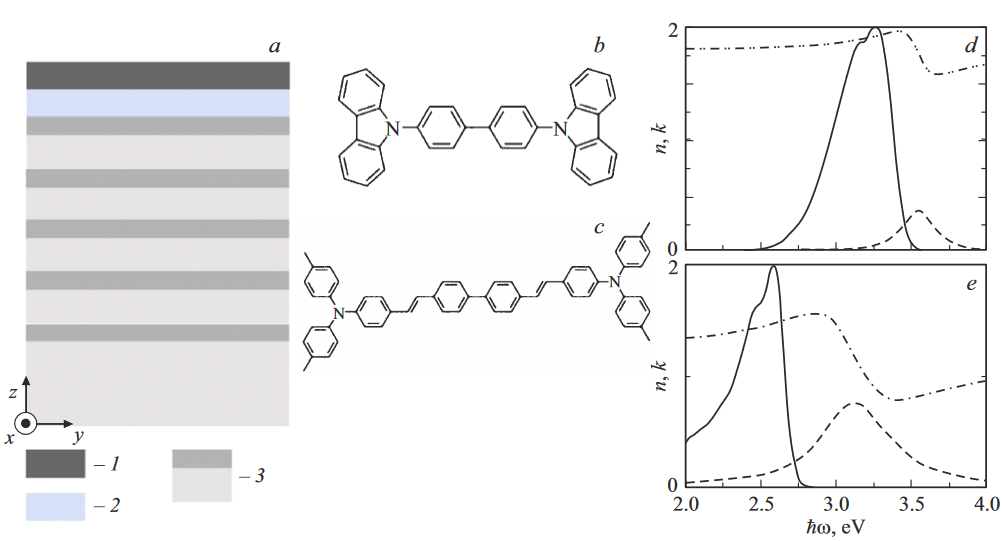
 Lasing in Tamm plasmon-based microcavities with intracavity metallic contacts and organic active areaMorozov K. M., Belonovski A. V., Girshova E. I. , and 1 more authorTechnical Physics Letters, Mar 2022
Lasing in Tamm plasmon-based microcavities with intracavity metallic contacts and organic active areaMorozov K. M., Belonovski A. V., Girshova E. I. , and 1 more authorTechnical Physics Letters, Mar 2022Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser design with organic light-emitting material 4,4’-bis[4-(di- p-tolylamino)styryl]biphenyl and intracavity metal contacts of two types are proposed. In the first design, two Bragg mirrors and two thin metal layers adjacent to the active region utilizes. In the second design one Bragg mirror with a thin metal layer and for the second mirror the thick metal layers uses. Mode structure, the spatial distribution of the optical fields, Purcell factor and the dependence of the output power on the pump power were calculated. Keywords: Tamm plasmon, organic semiconductor, vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, exciton.
@article{MorozovKM2022, title = {Lasing in Tamm plasmon-based microcavities with intracavity metallic contacts and organic active area}, volume = {48}, issn = {1726-7471}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.21883/TPL.2022.04.53161.19104}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.21883/tpl.2022.04.53161.19104}, number = {4}, journal = {Technical Physics Letters}, publisher = {Ioffe Institute Russian Academy of Sciences}, author = {M., Morozov K. and V., Belonovski A. and I., Girshova E. and V., Nikolaev V.}, year = {2022}, pages = {11}, } -
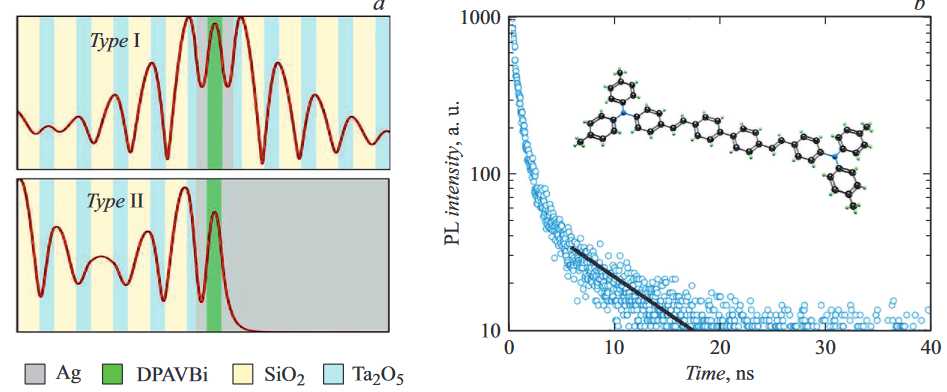
 Analysis of luminescence decay dynamics in metal-dielectric photonic structures with organic layersMorozov K.M., Belonovskii A. V., and Kaliteevski M. A.Semiconductors, Mar 2022
Analysis of luminescence decay dynamics in metal-dielectric photonic structures with organic layersMorozov K.M., Belonovskii A. V., and Kaliteevski M. A.Semiconductors, Mar 2022Metal-dielectric photonic structures with organic materials 4,4-bis(N-carbazolyl)-1,1-biphenyl and 4,4’-bis[4-(di-ptolylamino)styryl]biphenyl) as light emitting layers were investigated. The formation of the polaritonic modes in the investigated structures was experimentally demonstrated and a correlation between theoretical and experimental dispersion was shown. Was shown, that increase in interaction between organic exciton and optical mode leads to a significant decrease in the lower polariton emission bandwidth. Keywords: light-emitting layers, exciton, luminescence.
@article{MorozovKM2022_2, title = {Analysis of luminescence decay dynamics in metal-dielectric photonic structures with organic layers}, volume = {56}, issn = {1726-7315}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.21883/SC.2022.12.55149.4291}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.21883/sc.2022.12.55149.4291}, number = {12}, journal = {Semiconductors}, publisher = {Ioffe Institute Russian Academy of Sciences}, author = {K.M., Morozov and V., Belonovskii A. and A., Kaliteevski M.}, year = {2022}, pages = {904}, } -
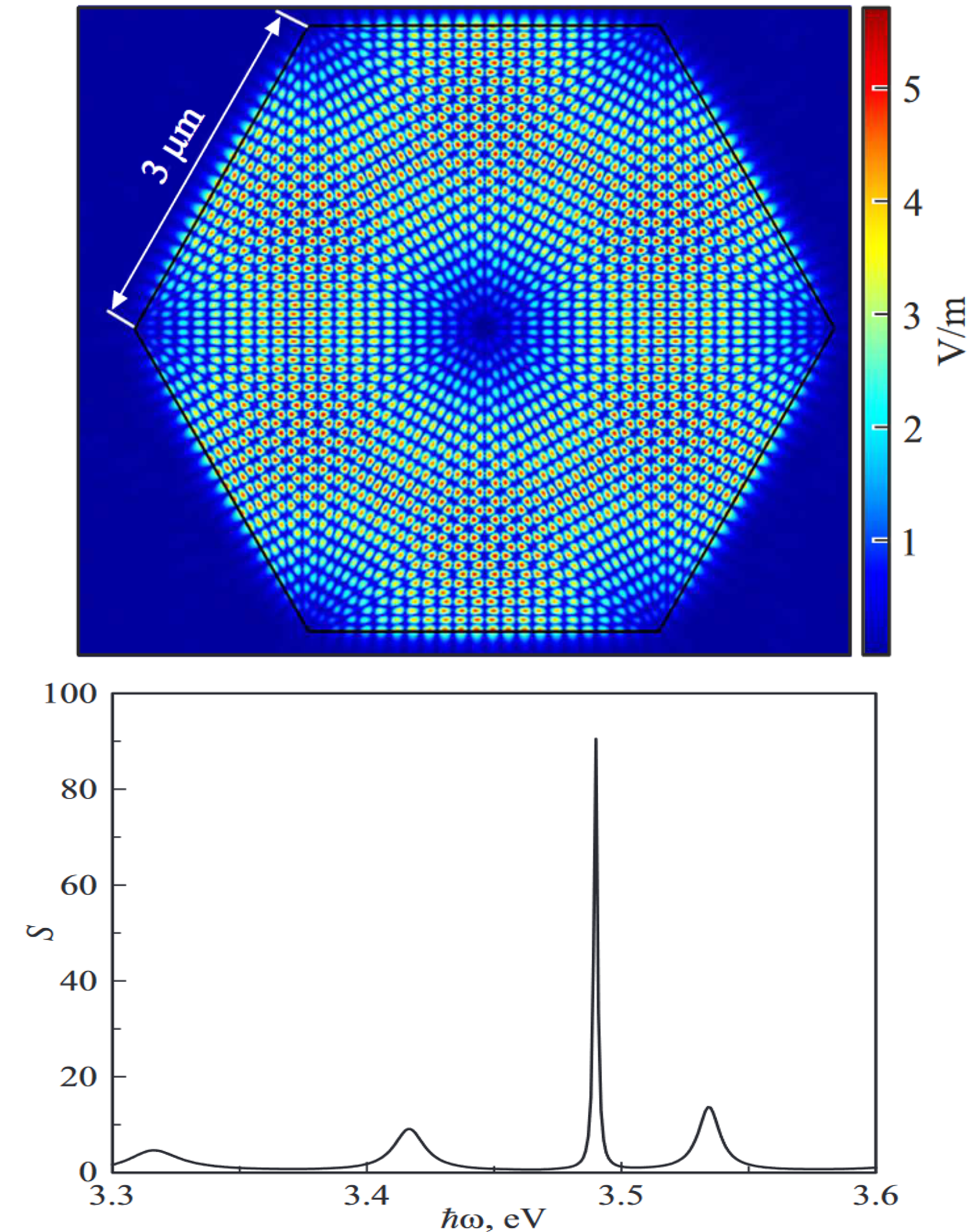 Analysis of exciton luminescence in GaN meso-cavity.Belonovski A. V., Morozov K. M., and Kotova L. V.Technical Physics Letters, Mar 2022
Analysis of exciton luminescence in GaN meso-cavity.Belonovski A. V., Morozov K. M., and Kotova L. V.Technical Physics Letters, Mar 2022We have considered the interaction of an exciton mode with photonic modes in a GaN structure several μm in size. A technique for obtaining spectra from such structures has been demonstrated. The cavity shape and dimensions most optimal for efficient light/matter interaction have been selected. The theoretical spectrum for the selected cavity has been obtained and analyzed Keywords: gallium nitride, exciton, meso-cavity, spectrum.
@article{BelonovskiAV2022, title = {Analysis of exciton luminescence in GaN meso-cavity.}, volume = {48}, issn = {1726-7471}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.21883/TPL.2022.01.52467.19033}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.21883/tpl.2022.01.52467.19033}, number = {1}, journal = {Technical Physics Letters}, publisher = {Ioffe Institute Russian Academy of Sciences}, author = {V., Belonovski A. and M., Morozov K. and V., Kotova L.}, year = {2022}, pages = {41}, }
2021
-
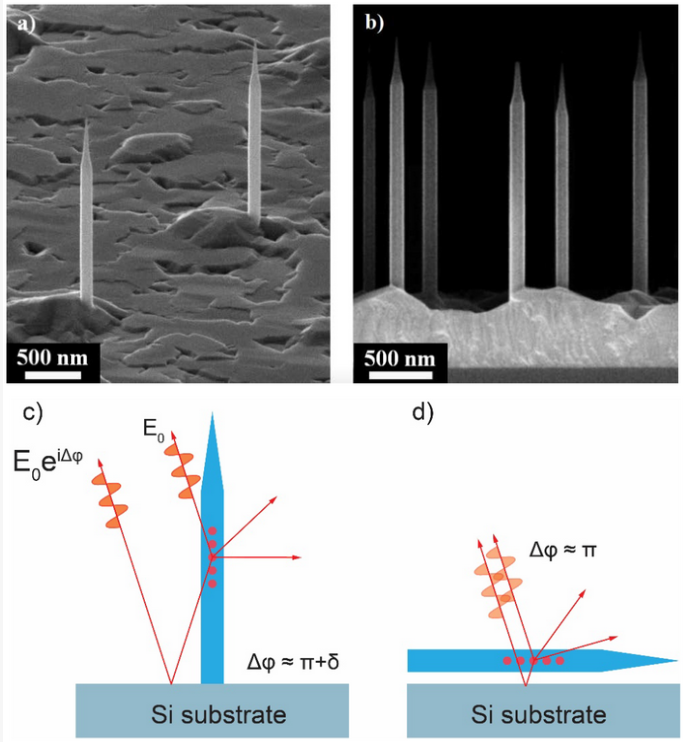 Purcell Effect and Beaming of Emission in Hybrid AlGaAs Nanowires with GaAs Quantum DotsRodion R. Reznik, George E. Cirlin, Konstantin P. Kotlyar , and 6 more authorsNanomaterials, Mar 2021
Purcell Effect and Beaming of Emission in Hybrid AlGaAs Nanowires with GaAs Quantum DotsRodion R. Reznik, George E. Cirlin, Konstantin P. Kotlyar , and 6 more authorsNanomaterials, Mar 2021Control of directionality of emissions is an important task for the realization of novel nanophotonic devices based on nanowires. Most of the existing approaches providing high directionality of the light emitted from nanowires are based on the utilization of the tapered shape of nanowires, serving as nanoantenna coupling with the light waveguided in nanowire and the directional output beam. Here we report the beaming of the emitted light with wavelength near 800 nm by naturally formed core-shell AlGaAs NW with multiply GaAs quantum dots (QDs) diameter 30 nm and height 10 nm, while the diameter of NW 130 nm, what does not support efficient emission into waveguided modes, including the mode HE11. Experimental measurements show that intensity of emission for directions in the vicinity of the axis of NW is about two orders of magnitude higher than for perpendicular directions. The developed theoretical approach allowed us to calculate the probability of spontaneous emission for various directions and into waveguided modes and showed that highly directional radiation can be provided by the intrinsic emission properties of cylindrical NW. Our results suggest that for the small diameter of NW, directional emissions are associated with an TM0 leaky mode (when electric field oriented in axial direction) and therefore manifests in an existence of axial electric dipole transitions in quantum dots.
@article{nano11112894, author = {Reznik, Rodion R. and Cirlin, George E. and Kotlyar, Konstantin P. and Ilkiv, Igor V. and Akopian, Nika and Leandro, Lorenzo and Nikolaev, Valentin V. and Belonovski, Alexey V. and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, title = {Purcell Effect and Beaming of Emission in Hybrid AlGaAs Nanowires with GaAs Quantum Dots}, journal = {Nanomaterials}, volume = {11}, year = {2021}, number = {11}, article-number = {2894}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/11/11/2894}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {0EnyYjriUFMC}, pubmedid = {34835659}, issn = {2079-4991}, doi = {10.3390/nano11112894}, } -
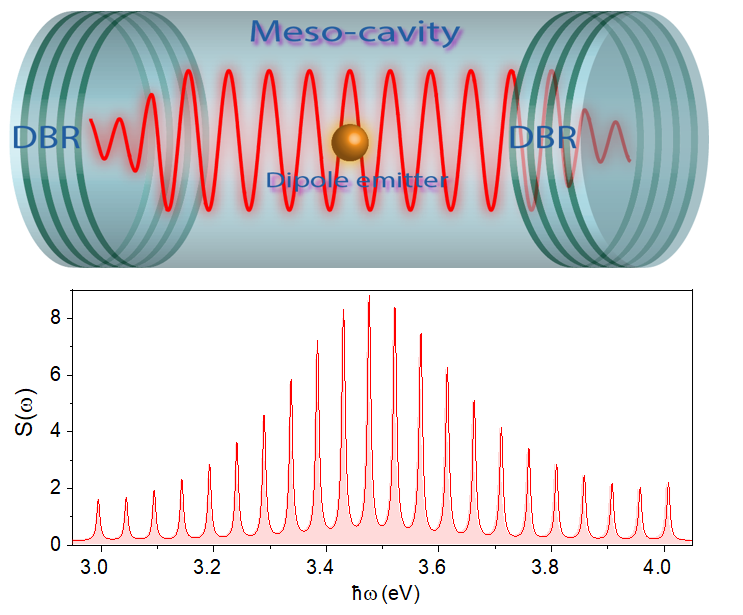 Quantum analysis of luminescence of an exciton in a meso-cavityAlexey V. Belonovski, Konstantin M. Morozov, Elizaveta I. Girshova , and 2 more authorsOpt. Express, Jun 2021
Quantum analysis of luminescence of an exciton in a meso-cavityAlexey V. Belonovski, Konstantin M. Morozov, Elizaveta I. Girshova , and 2 more authorsOpt. Express, Jun 2021Interaction of cavity modes with an exciton in a meso-cavity (the structure supporting several cavity modes separated by an energy interval comparable to Rabi-splitting of an exciton and cavity modes) has been analyzed using a quantum-mechanical approach. Simultaneous interaction of an exciton and several cavity modes results in few novel effects such as ladder-like increase of the exciton population in the system, quantum beating and non-monotonic dependence of the ground polariton state in the system on the pumping.
@article{Belonovski:21, author = {Belonovski, Alexey V. and Morozov, Konstantin M. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and Pozina, Galia and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, journal = {Opt. Express}, keywords = {Bragg reflectors; Dielectric mirrors; Optical pumping; Organic materials; Quantum beats; Quantum electrodynamics}, number = {13}, pages = {20724--20734}, publisher = {Optica Publishing Group}, title = {Quantum analysis of luminescence of an exciton in a meso-cavity}, volume = {29}, month = jun, year = {2021}, url = {https://opg.optica.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-29-13-20724}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {hqOjcs7Dif8C}, doi = {10.1364/OE.420277}, } -
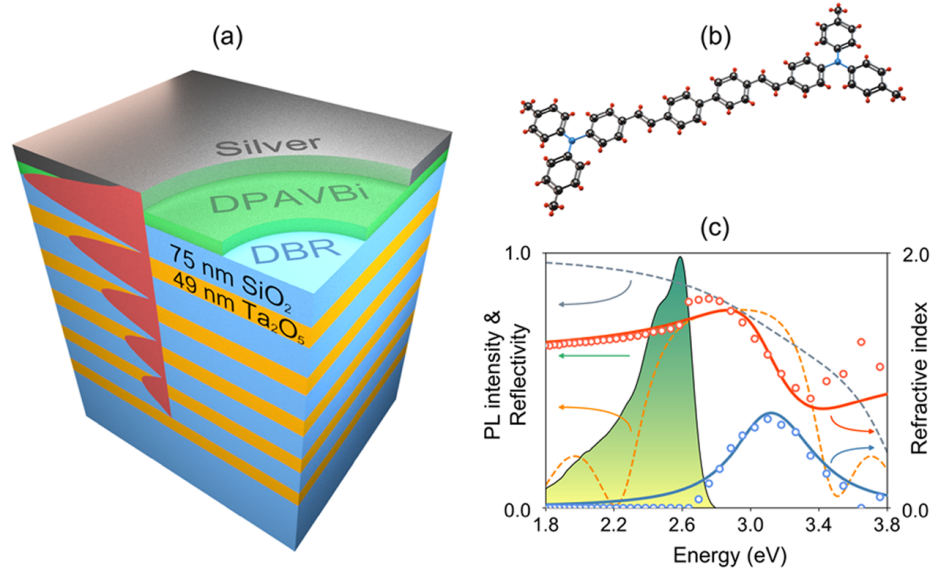 Opposite Sign of Polarization Splitting in Ultrastrongly Coupled Organic Tamm Plasmon StructuresKonstantin M. Morozov, Piotr Pander, Larissa G. Franca , and 8 more authorsThe Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Jun 2021
Opposite Sign of Polarization Splitting in Ultrastrongly Coupled Organic Tamm Plasmon StructuresKonstantin M. Morozov, Piotr Pander, Larissa G. Franca , and 8 more authorsThe Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Jun 2021The properties of the ultrastrongly coupled Tamm plasmon cavity filled with a high-oscillator-strength organic material DPAVBi (4,4′-bis[4-(di-p-tolylamino)styryl]biphenyl) are studied using theoretical and experimental methods. An analytical model predicts the opposite sign of polarization splitting for the lower and upper polariton cases and a giant absolute value of the splitting. A set of organic Tamm plasmon cavities with different detuning parameters are fabricated. We demonstrate that all structures are operating in the ultrastrong coupling regime: the values of the Rabi splitting are close to a 20% fraction of the exciton energy. The measured angle-dependent reflectivity spectra structure for both transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) polarizations confirm the predicted theoretical model. We obtained a giant value of the polarization splitting of up to 180 meV for both polariton branches. We believe that it is the first demonstration of such peculiar polarization splitting behavior of polaritons in the ultrastrong coupling regime.
@article{doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c02432, author = {Morozov, Konstantin M. and Pander, Piotr and Franca, Larissa G. and Belonovski, Alexey V. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and Ivanov, Konstantin A. and Livshits, Daniil A. and Selenin, Nikita V. and Pozina, Galia and Monkman, Andrew P. and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, title = {Opposite Sign of Polarization Splitting in Ultrastrongly Coupled Organic Tamm Plasmon Structures}, journal = {The Journal of Physical Chemistry C}, volume = {125}, number = {15}, pages = {8376-8381}, year = {2021}, doi = {10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c02432}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c02432}, eprint = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c02432}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {9yKSN-GCB0IC}, } -
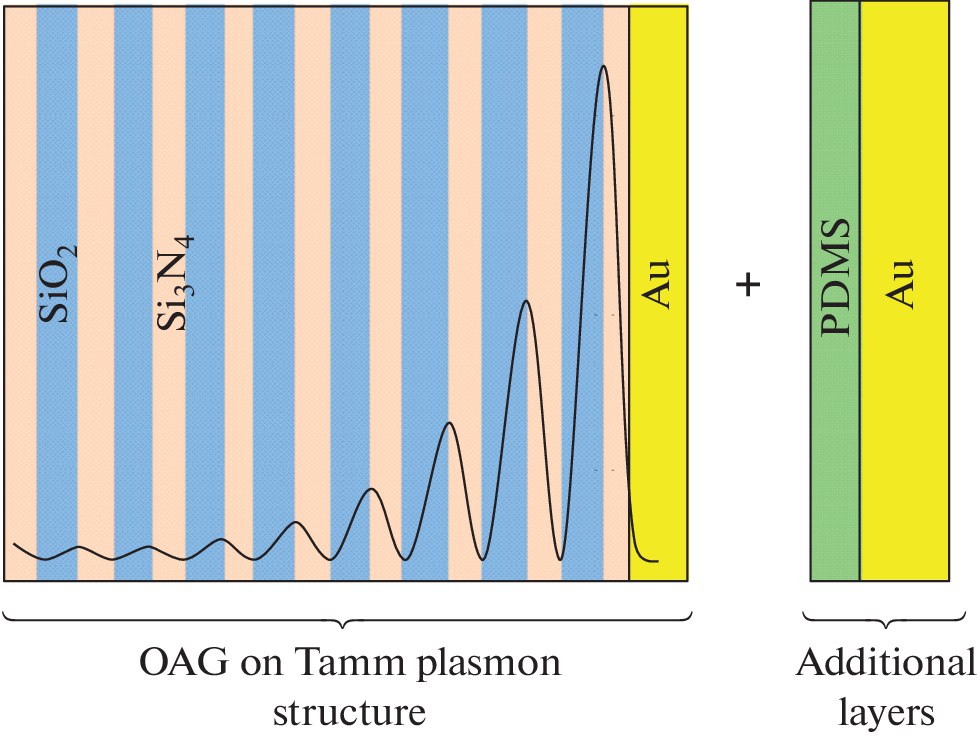 An Optoacoustic Ultrasound Generator Based on a Tamm Plasmon and Organic Active Layer StructureE. I. Girshova, E. P. Mikitchuk, A. V. Belonovskii , and 2 more authorsTechnical Physics Letters, Apr 2021
An Optoacoustic Ultrasound Generator Based on a Tamm Plasmon and Organic Active Layer StructureE. I. Girshova, E. P. Mikitchuk, A. V. Belonovskii , and 2 more authorsTechnical Physics Letters, Apr 2021Improvement has been considered of an optoacoustic generator based on a structure with a Tamm plasmon as an active medium by means of the addition of an organic material (polydimethylsiloxane) layer with an extremely high thermal expansion coefficient. The simulation of the structure characteristics has been shown that the use of polydimethylsiloxane as an additional layer in the optoacoustic transducer structure is appropriate at frequencies up to 50 MHz. We have also shown that the addition of an organic layer leads to an increase in the efficiency of the optoacoustic transformation by four orders.
@article{Girshova2021, title = {An Optoacoustic Ultrasound Generator Based on a Tamm Plasmon and Organic Active Layer Structure}, volume = {47}, issn = {1090-6533}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063785021040076}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {5nxA0vEk-isC}, doi = {10.1134/s1063785021040076}, number = {4}, journal = {Technical Physics Letters}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Girshova, E. I. and Mikitchuk, E. P. and Belonovskii, A. V. and Morozov, K. M. and Ivanov, K. A.}, year = {2021}, month = apr, pages = {336–340}, } -
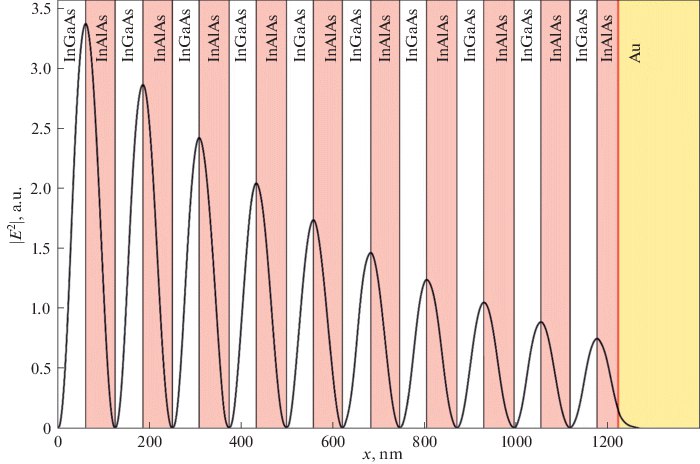 Optical and Thermal Properties of a Hybrid Metal–Dielectric ReflectorE. A. Kharitonova, E. I. Girshova, A. V. Belonovskii , and 3 more authorsTechnical Physics Letters, Jan 2021
Optical and Thermal Properties of a Hybrid Metal–Dielectric ReflectorE. A. Kharitonova, E. I. Girshova, A. V. Belonovskii , and 3 more authorsTechnical Physics Letters, Jan 2021The thermal and optical properties of a combined (hybrid) metal–dielectric reflector comprising a gold layer and distributed Bragg reflector composed of alternating In0.52Al0.48As/In0.53Ga0.47As bilayers are considered. It is established that a high coefficient of reflection of the hybrid structure can be achieved at low absorption in the metal and relatively small total thickness of the dielectric reflector.
@article{Kharitonova2021, title = {Optical and Thermal Properties of a Hybrid Metal–Dielectric Reflector}, volume = {47}, issn = {1090-6533}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063785021010223}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {Se3iqnhoufwC}, doi = {10.1134/s1063785021010223}, number = {1}, journal = {Technical Physics Letters}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Kharitonova, E. A. and Girshova, E. I. and Belonovskii, A. V. and Morozov, K. M. and Ivanov, K. A. and Simchuk, O. I.}, year = {2021}, month = jan, pages = {61–64}, }
2020
-
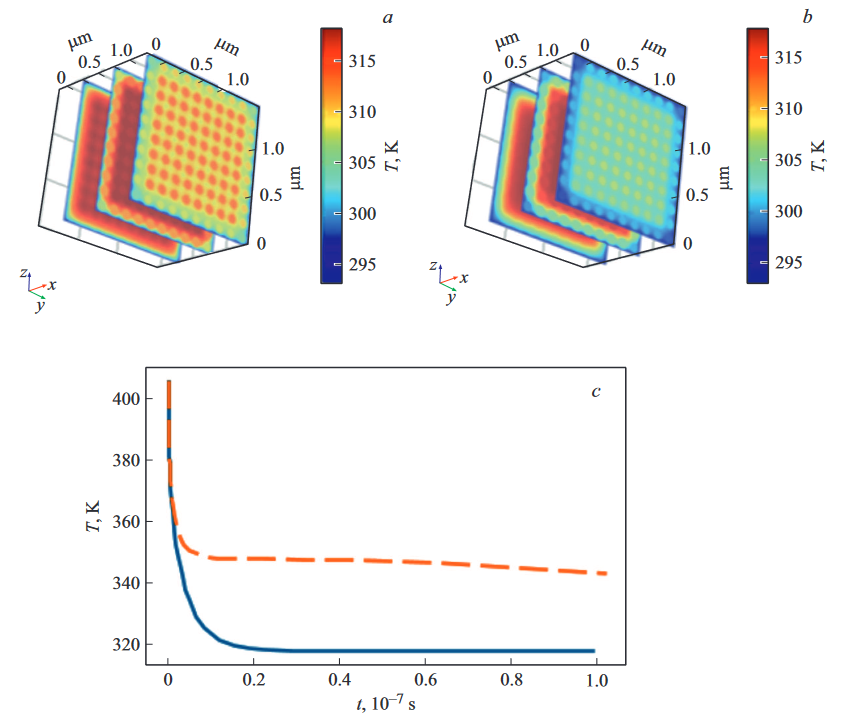
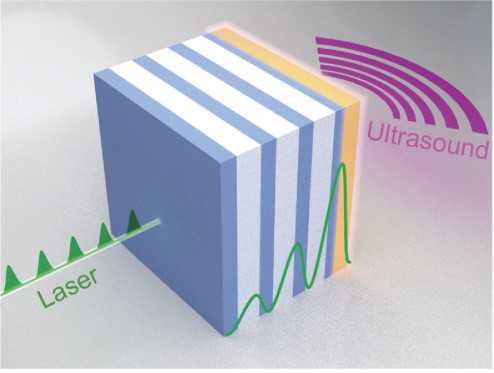 Proposal for a photoacoustic ultrasonic generator based on Tamm plasmon structuresElizaveta I. Girshova, Alena P. Mikitchuk, Alexey V. Belonovski , and 6 more authorsOpt. Express, Aug 2020
Proposal for a photoacoustic ultrasonic generator based on Tamm plasmon structuresElizaveta I. Girshova, Alena P. Mikitchuk, Alexey V. Belonovski , and 6 more authorsOpt. Express, Aug 2020The scheme of a generation of ultrasound waves based on optically excited Tamm plasmon structures is proposed. It is shown that Tamm plasmon structures can provide total absorption of a laser pulse with arbitrary wavelength in a metallic layer providing the possibility of the use of an infrared semiconductor laser for the excitation of ultrasound waves. Laser pulse absorption, heat transfer and dynamical properties of the structure are modeled, and the optimal design of the structure is found. It is demonstrated that the Tamm plasmon-based photoacoustic generator can emit ultrasound waves in the frequency band up to 100 MHz with predefined frequency spectrum.
@article{Girshova:20, author = {Girshova, Elizaveta I. and Mikitchuk, Alena P. and Belonovski, Alexey V. and Morozov, Konstantin M. and Ivanov, Konstantin A. and Pozina, Galia and Kozadaev, Konstantin V. and Egorov, Anton Yu. and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, journal = {Opt. Express}, keywords = {Infrared lasers; Laser systems; Metal nanoparticles; Organic materials; Semiconductor lasers; Thin films}, number = {18}, pages = {26161--26169}, publisher = {Optica Publishing Group}, title = {Proposal for a photoacoustic ultrasonic generator based on Tamm plasmon structures}, volume = {28}, month = aug, year = {2020}, url = {https://opg.optica.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-28-18-26161}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {qjMakFHDy7sC}, doi = {10.1364/OE.400639}, } -
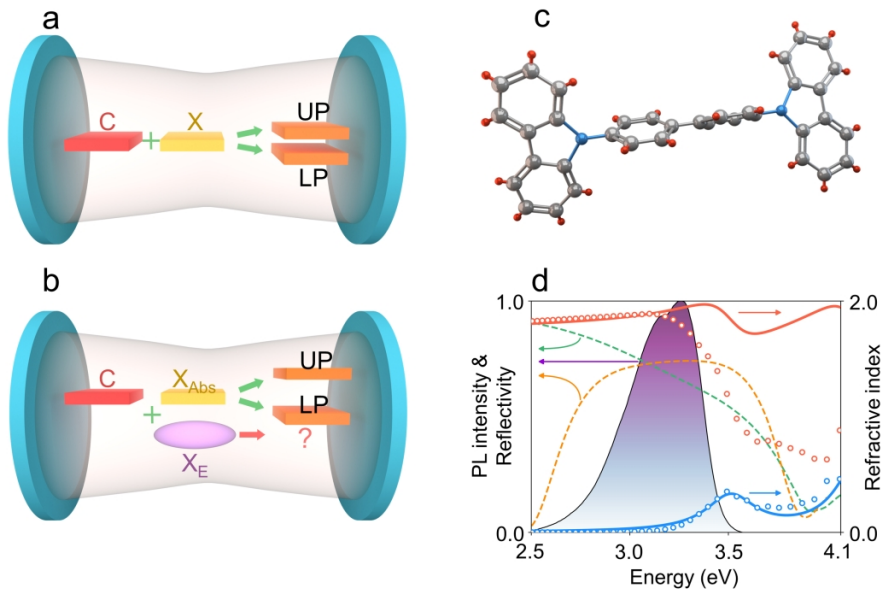 Efficient UV Luminescence from Organic-Based Tamm Plasmon Structures Emitting in the Strong-Coupling RegimeKonstantin M. Morozov, Konstantin A. Ivanov, Alexey V. Belonovski , and 10 more authorsThe Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Aug 2020
Efficient UV Luminescence from Organic-Based Tamm Plasmon Structures Emitting in the Strong-Coupling RegimeKonstantin M. Morozov, Konstantin A. Ivanov, Alexey V. Belonovski , and 10 more authorsThe Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Aug 2020Excitons in organic semiconductors possessing a large oscillator strength demonstrate strong coupling with cavity modes at room temperature. A large Stokes shift in some organic semiconductors enriches and complicates the picture of the emission in strongly coupled systems of organic excitons and light. Here, we demonstrate strong coupling of excitons in 4,4-bis(N-carbazolyl)-1,1-biphenyl (CBP) and Tamm plasmons in the ultraviolet (UV) band, accompanied by a bright emission from the structure. Reflection measurements demonstrate the pronounced formation of the lower and upper polariton modes with Rabi splitting of the magnitude of 0.3 eV, and the emission peak experiences a substantial red shift with respect to the lower polariton mode. Both radiative and nonradiative decay rates in the Tamm plasmon CBP structure are increased with respect to a bare CBP. Such peculiar behavior is attributed to the simultaneous manifestation of strong coupling and weak coupling of the CBP molecule emitters to the Tamm plasmons.
@article{doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05091, author = {Morozov, Konstantin M. and Ivanov, Konstantin A. and Belonovski, Alexey V. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and Pereira, Daniel de Sa and Menelaou, Christopher and Pander, Piotr and Franca, Larissa G. and Monkman, Andrew P. and Pozina, Galia and Livshits, Daniil A. and Selenin, Nikita V. and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, title = {Efficient UV Luminescence from Organic-Based Tamm Plasmon Structures Emitting in the Strong-Coupling Regime}, journal = {The Journal of Physical Chemistry C}, volume = {124}, number = {39}, pages = {21656-21663}, year = {2020}, doi = {10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05091}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05091}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {2osOgNQ5qMEC}, eprint = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05091}, } -
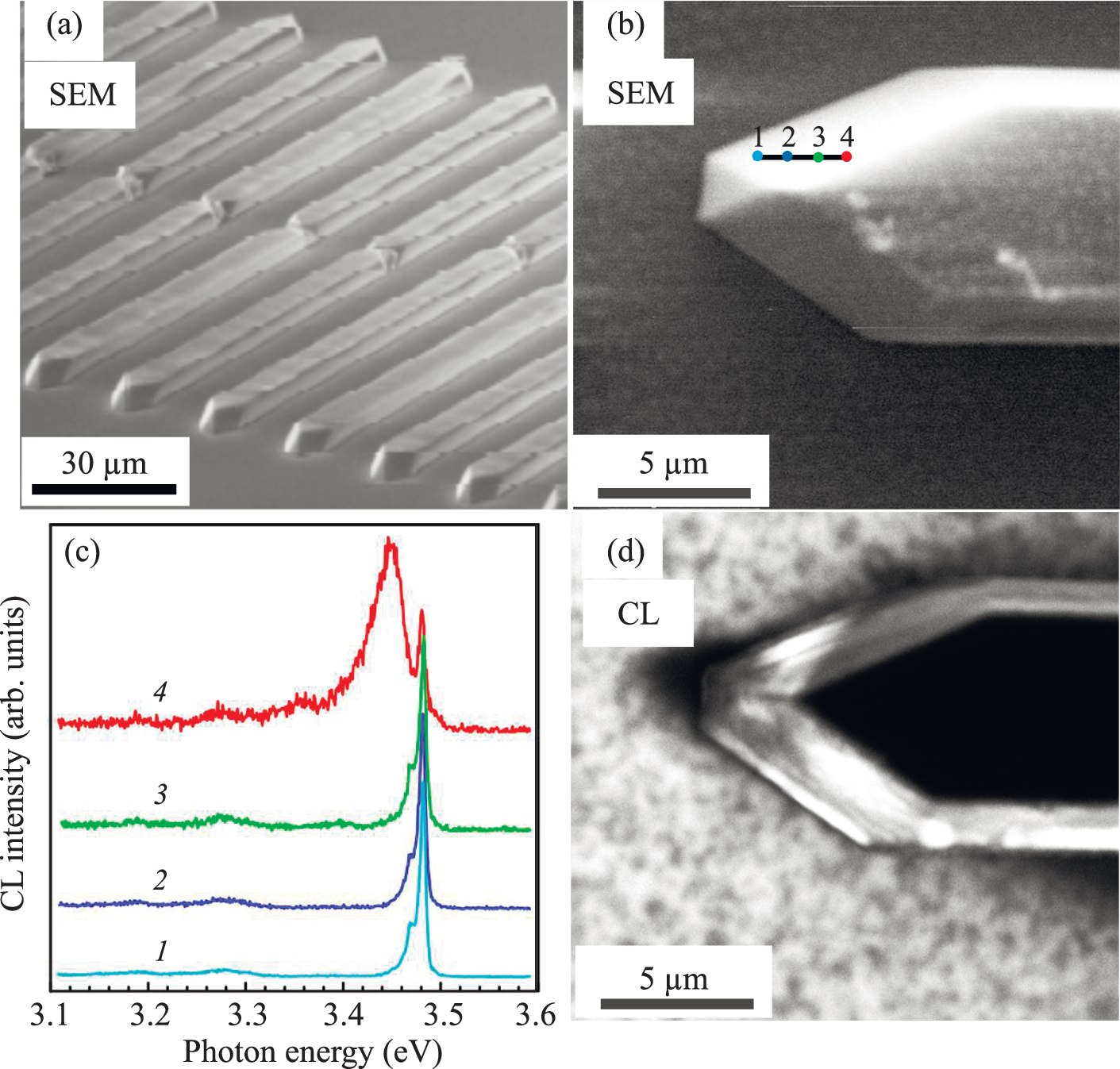
 Emission Properties of GaN Planar Hexagonal MicrocavitiesGalia Pozina, Carl Hemmingsson, Alexei V. Belonovskii , and 8 more authorsphysica status solidi (a), Aug 2020
Emission Properties of GaN Planar Hexagonal MicrocavitiesGalia Pozina, Carl Hemmingsson, Alexei V. Belonovskii , and 8 more authorsphysica status solidi (a), Aug 2020Fabrication of microcavities based on III-nitrides is challenging due to difficulties with the coherent growth of heterostructures having a large number of periods, at the same time keeping a good precision in terms of thickness and composition of the alloy. A planar design for GaN microresonators supporting whispering gallery modes is suggested. GaN hexagonal microstructures are fabricated by selective-area metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy using focused ion beam for mask patterning. Low-temperature cathodoluminescence spectra measured with a high spatial resolution demonstrate two dominant emission lines in the near bandgap region. These lines merge at room temperature into a broad emission band peaking at ≈3.3 eV, which is shifted toward lower energies compared with the reference excitonic spectrum measured for the GaN layer. A numerical analysis of exciton–polariton modes shows that some strongly localized cavity modes can have high Purcell coefficients and can strongly interact with the GaN exciton.
@article{https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201900894, author = {Pozina, Galia and Hemmingsson, Carl and Belonovskii, Alexei V. and Levitskii, Iaroslav V. and Mitrofanov, Maxim I. and Girshova, Elizaveta I. and Ivanov, Konstantin A. and Rodin, Sergey N. and Morozov, Konstantin M. and Evtikhiev, Vadim P. and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, title = {Emission Properties of GaN Planar Hexagonal Microcavities}, journal = {physica status solidi (a)}, volume = {217}, number = {14}, pages = {1900894}, keywords = {cavity modes, GaN hexagonal microstructures, planar microcavities, Purcell factor, selective area epitaxy}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201900894}, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pssa.201900894}, eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/pssa.201900894}, google_scholar_id = {YsMSGLbcyi4C}, year = {2020}, } -
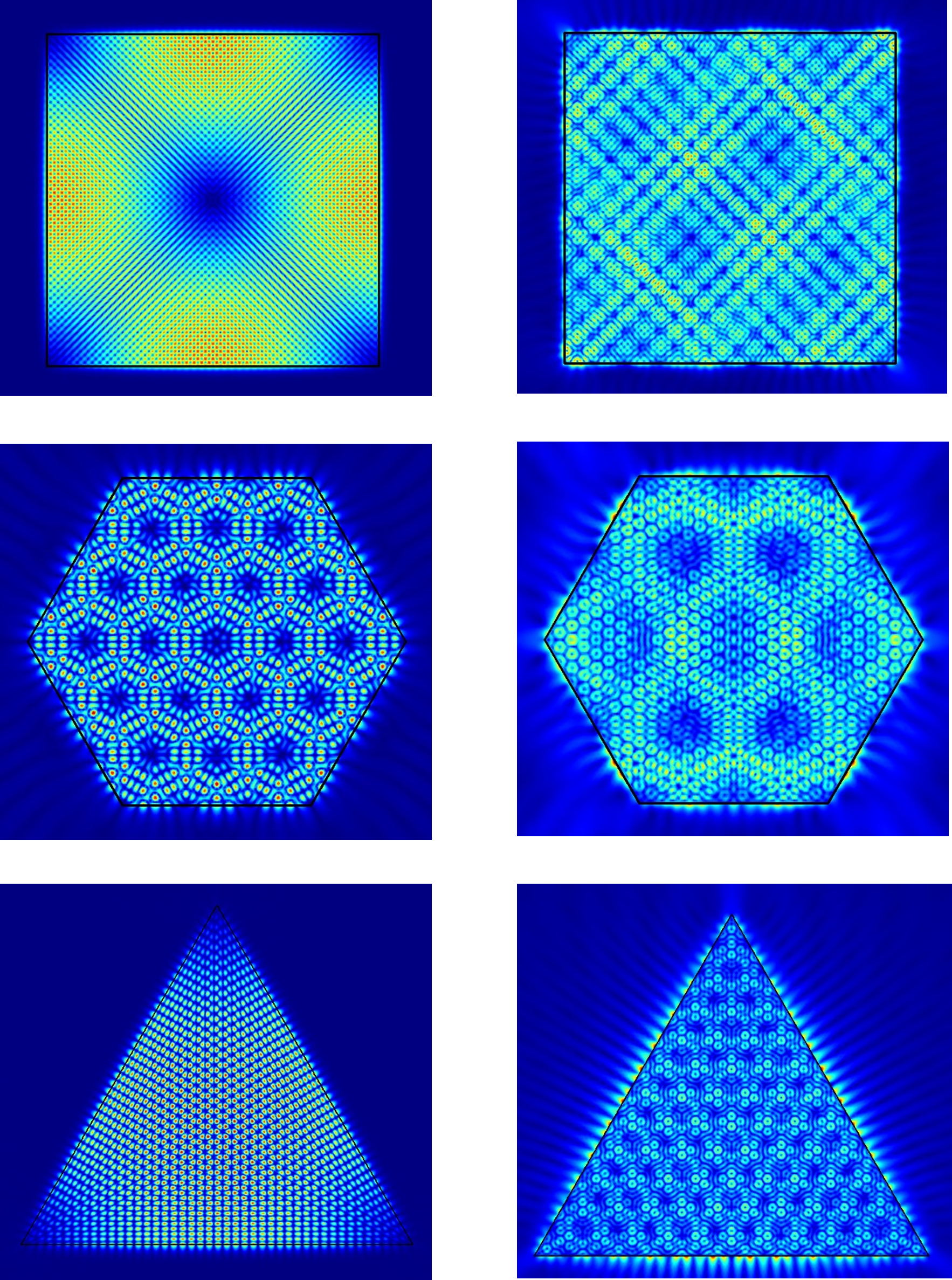 Weak and strong coupling of photons and excitons in planar meso-cavitiesAlexey V. Belonovski, Iaroslav V. Levitskii, Konstantin M. Morozov , and 2 more authorsOpt. Express, Apr 2020
Weak and strong coupling of photons and excitons in planar meso-cavitiesAlexey V. Belonovski, Iaroslav V. Levitskii, Konstantin M. Morozov , and 2 more authorsOpt. Express, Apr 2020The interaction of an exciton and cavity modes is considered in planar meso-cavities, which have lateral sizes corresponding to few wavelengths. In meso-cavities, the frequency interval between the optical modes is comparable or smaller than the value of the Rabi splitting between the exciton and the optical modes. The Hamiltonian of the interaction between the exciton and the cavity modes is constructed, and it is shown that such an interaction between the cavity modes and the exciton can occur both in weak and in strong coupling regimes. The latter case can be accompanied by a pronounced splitting of the emission peaks as shown for modelled meso-cavities of triangular, square and hexagonal shapes, where it is demonstrated that Q-factors for the adjacent cavity modes as well as the strength of interaction with excitons can differ by few orders of magnitude.
@article{Belonovski:20, author = {Belonovski, Alexey V. and Levitskii, Iaroslav V. and Morozov, Konstantin M. and Pozina, Galia and Kaliteevski, Mikhail A.}, journal = {Opt. Express}, keywords = {Absorption spectroscopy; Microcavities; Modes; Photon counting; Quantum wells; Refractive index}, number = {9}, pages = {12688--12698}, publisher = {Optica Publishing Group}, title = {Weak and strong coupling of photons and excitons in planar meso-cavities}, volume = {28}, month = apr, year = {2020}, url = {https://opg.optica.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-28-9-12688}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {u5HHmVD_uO8C}, doi = {10.1364/OE.388899}, } -
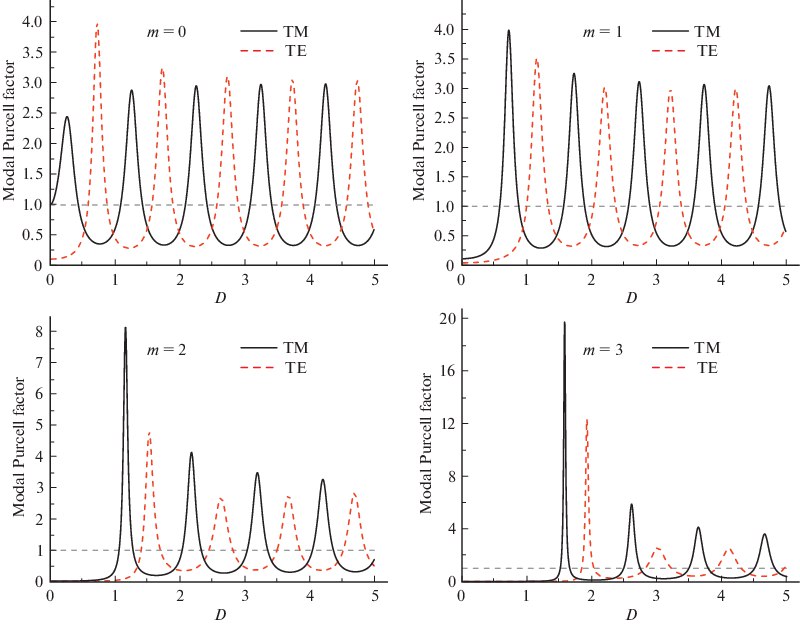 Scattering Matrix Method for Calculating the Spontaneous-Emission Probability in Cylindrically Symmetric StructuresV. V. Nikolaev, K. A. Ivanov, K. M. Morozov , and 1 more authorSemiconductors, Jun 2020
Scattering Matrix Method for Calculating the Spontaneous-Emission Probability in Cylindrically Symmetric StructuresV. V. Nikolaev, K. A. Ivanov, K. M. Morozov , and 1 more authorSemiconductors, Jun 2020A method is developed for analyzing spontaneous-emission modification in cylindrically symmetric structures. A matrix method is developed for cylindrical structures. General expressions for the radiative-recombination rate are derived for an emitter placed at any point on the structure. Quantitative indicators for estimating radiative-recombination enhancement and suppression are determined; they can be considered as modal Purcell factors. An expression for the total Purcell factor is derived for an emission direction perpendicular to the symmetry axes of the medium; as well as an expression for the integral (total) Purcell factor for the emitter at the symmetry axis.
@article{Nikolaev2020, title = {Scattering Matrix Method for Calculating the Spontaneous-Emission Probability in Cylindrically Symmetric Structures}, volume = {54}, issn = {1090-6479}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620070106}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {d1gkVwhDpl0C}, doi = {10.1134/s1063782620070106}, number = {7}, journal = {Semiconductors}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Nikolaev, V. V. and Ivanov, K. A. and Morozov, K. M. and Belonovski, A. V.}, year = {2020}, month = jun, pages = {765–773}, } -
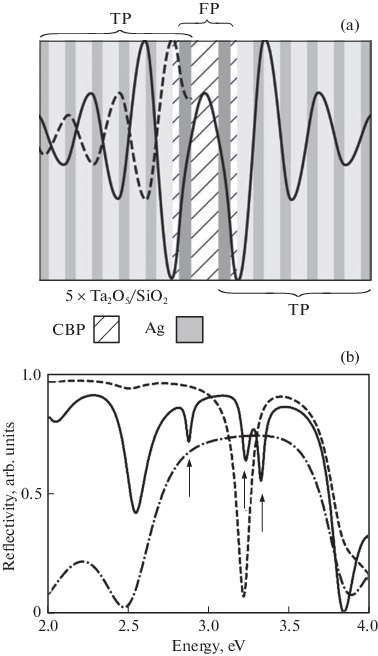 Properties of a Tamm-Plasmon-Based Microcavity with Metal Intracavity Layers and an Organic Active RegionK. M. Morozov, A. V. Belonovskii, E. I. Girshova , and 2 more authorsSemiconductors, Mar 2020
Properties of a Tamm-Plasmon-Based Microcavity with Metal Intracavity Layers and an Organic Active RegionK. M. Morozov, A. V. Belonovskii, E. I. Girshova , and 2 more authorsSemiconductors, Mar 2020The properties of a microcavity structure with metal intracavity layers and an organic active region (based on the low-molecular-weight compound 4,4’-Bis(N-carbazolyl)-1,1’-biphenyl (CBP)) are analyzed theoretically. The structure under study consists of a CBP layer of a given thickness sandwiched between two silver layers, two thin phase-matching CBP layers (dph = 26 nm), and two quarter-wave Bragg reflectors. It is shown that hybrid modes localized in the central layer of the structure can significantly increase the luminescence decay rate of an organic emitter due to the Purcell effect. It is found that the spectral positions of the hybrid modes are shifted because of their interaction with exciton resonance in CBP. This may indicate the emergence of a strong coupling regime.
@article{Morozov2020, title = {Properties of a Tamm-Plasmon-Based Microcavity with Metal Intracavity Layers and an Organic Active Region}, volume = {54}, issn = {1090-6479}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S106378262003015X}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {_FxGoFyzp5QC}, doi = {10.1134/s106378262003015x}, number = {3}, journal = {Semiconductors}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Morozov, K. M. and Belonovskii, A. V. and Girshova, E. I. and Ivanov, K. A. and Kaliteevski, M. A.}, year = {2020}, month = mar, pages = {350–354}, } -
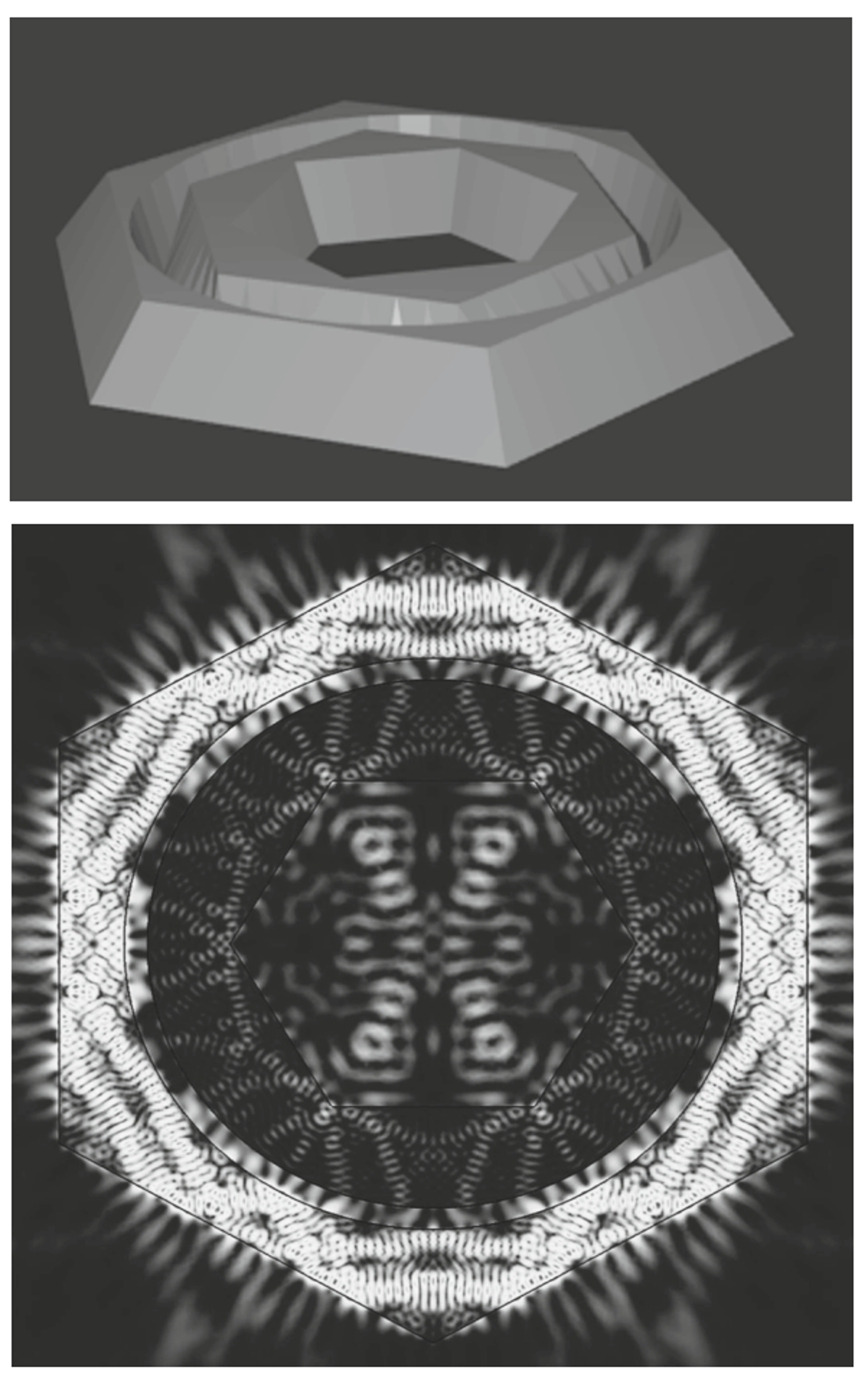 Strong Coupling of Excitons in Hexagonal GaN MicrocavitiesA. V. Belonovskii, G. Pozina, I. V. Levitskii , and 7 more authorsSemiconductors, Jan 2020
Strong Coupling of Excitons in Hexagonal GaN MicrocavitiesA. V. Belonovskii, G. Pozina, I. V. Levitskii , and 7 more authorsSemiconductors, Jan 2020The GaN planar hexagonal microcavities are grown by the selective vapor-phase epitaxy technique. The spectra are measured by the low-temperature cathodoluminescence method using a scanning electron microscope. The obtained spectra show a huge Rabi splitting ( 100 meV). Numerical simulation of the spatial distribution of the intensities of modes in a hexagonal cavity is carried out. Certain modes can have a high spatial localization leading to strong coupling with the exciton and huge Rabi splitting. The fraction of excitons in polariton modes, which correlates with the intensity of exciton radiation associated with these modes, is theoretically calculated for hexagonal-shaped microcavities. Thus, the form of the dependence of the radiation probability on the eigenfrequencies of the structure is obtained.
@article{Belonovskii2020, title = {Strong Coupling of Excitons in Hexagonal GaN Microcavities}, volume = {54}, issn = {1090-6479}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620010042}, google_scholar_id = {WF5omc3nYNoC}, doi = {10.1134/s1063782620010042}, number = {1}, journal = {Semiconductors}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Belonovskii, A. V. and Pozina, G. and Levitskii, I. V. and Morozov, K. M. and Mitrofanov, M. I. and Girshova, E. I. and Ivanov, K. A. and Rodin, S. N. and Evtikhiev, V. P. and Kaliteevski, M. A.}, year = {2020}, month = jan, pages = {127–130}, }
2019
-
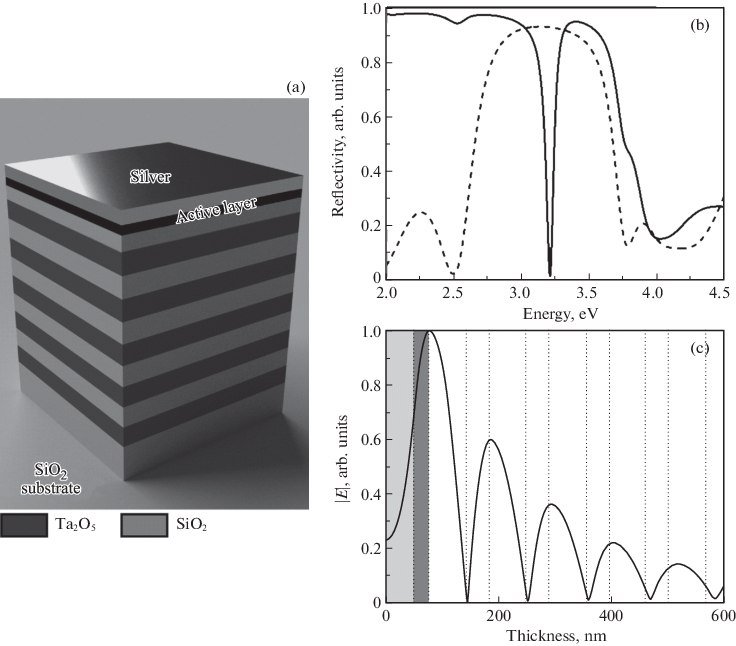 Interaction of a Tamm Plasmon and Exciton in an Organic Material in the Strong Coupling ModeK. M. Morozov, A. V. Belonovskii, K. A. Ivanov , and 2 more authorsSemiconductors, Oct 2019
Interaction of a Tamm Plasmon and Exciton in an Organic Material in the Strong Coupling ModeK. M. Morozov, A. V. Belonovskii, K. A. Ivanov , and 2 more authorsSemiconductors, Oct 2019The interaction of a Tamm plasmon with an exciton in an organic material in the strong coupling mode is investigated theoretically. The structure consists of five pairs of layers of silicon oxide and tantalum oxide, an organic light-emitting layer of 4,4’-bis(N-carbazolyl)-1,1’-biphenyl, and a silver layer. It is shown that the splitting of polariton modes (Rabi splitting) with a magnitude of >400 meV can occur in such a structure, which can be accompanied by an increase in the luminescence bandwidth up to 700 meV.
@article{Morozov2019, title = {Interaction of a Tamm Plasmon and Exciton in an Organic Material in the Strong Coupling Mode}, volume = {53}, issn = {1090-6479}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063782619100142}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {IjCSPb-OGe4C}, doi = {10.1134/s1063782619100142}, number = {10}, journal = {Semiconductors}, publisher = {Pleiades Publishing Ltd}, author = {Morozov, K. M. and Belonovskii, A. V. and Ivanov, K. A. and Girshova, E. I. and Kaliteevski, M. A.}, year = {2019}, month = oct, pages = {1314–1317}, } -
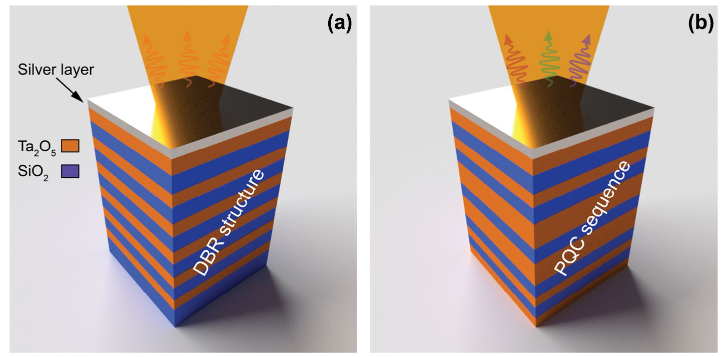 Emission enhancement in hybrid Tamm plasmon/photonic quasicrystal structureKonstantin M. Morozov, Konstantin A. Ivanov, Aleksei V. Belonovskii , and 1 more authorSN Applied Sciences, Oct 2019
Emission enhancement in hybrid Tamm plasmon/photonic quasicrystal structureKonstantin M. Morozov, Konstantin A. Ivanov, Aleksei V. Belonovskii , and 1 more authorSN Applied Sciences, Oct 2019We have theoretically demonstrated that Tamm plasmon structure with photonic quasicrystal instead of usual distributed Bragg reflector can support hybrid Tamm plasmon-like optical eigenstates. The model structure consists of a SiO2/Ta2O5 optical Fibonacci system with a thin silver layer on the top. F7-based hybrid cavity was analyzed by means of calculation reflectivity spectrum and electric field profiles of the localized states. Also, evaluation of the modal Purcell factor for hybrid structure demonstrates significant enhancing of spontaneous decay rate for emitter coupled with Tamm plasmon-like states. The results can be used in fabrication of high-efficient organic-based light emission systems.
@article{Morozov2019_2, title = {Emission enhancement in hybrid Tamm plasmon/photonic quasicrystal structure}, volume = {1}, issn = {2523-3971}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1375-6}, google_scholar_id = {W7OEmFMy1HYC}, doi = {10.1007/s42452-019-1375-6}, number = {11}, journal = {SN Applied Sciences}, publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC}, author = {Morozov, Konstantin M. and Ivanov, Konstantin A. and Belonovskii, Aleksei V. and Girshova, Elizaveta I.}, year = {2019}, month = oct, } -
 The interaction of an exciton and several optical modes in layer of GaAsA V Belonovskii, K M Morozov, and M V FetisovaJournal of Physics: Conference Series, Dec 2019
The interaction of an exciton and several optical modes in layer of GaAsA V Belonovskii, K M Morozov, and M V FetisovaJournal of Physics: Conference Series, Dec 2019Theoretically, we calculated exciton fraction in polariton modes, which correlates with the intensity of the exciton radiation associated with these modes for several microcavities. Thus, we obtained the form of the dependence of the radiation probability on the eigenfrequencies of the structure.
@article{Belonovskii2019, title = {The interaction of an exciton and several optical modes in layer of GaAs}, volume = {1410}, issn = {1742-6596}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1410/1/012151}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.1088/1742-6596/1410/1/012151}, number = {1}, journal = {Journal of Physics: Conference Series}, publisher = {IOP Publishing}, author = {Belonovskii, A V and Morozov, K M and Fetisova, M V}, year = {2019}, month = dec, pages = {012151}, } -
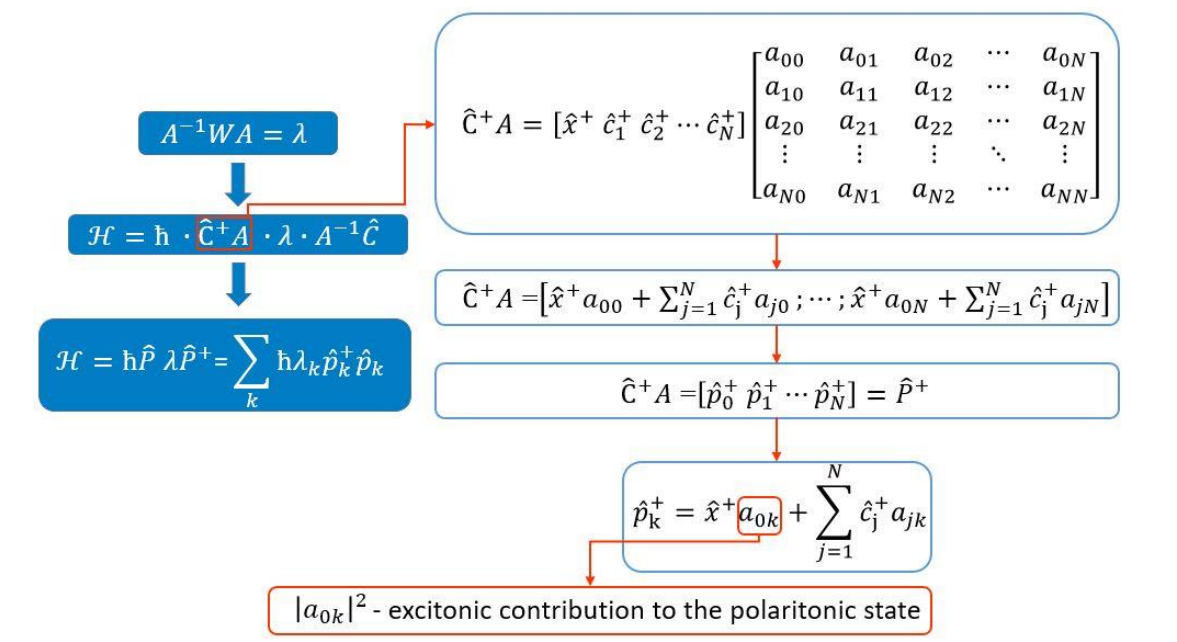
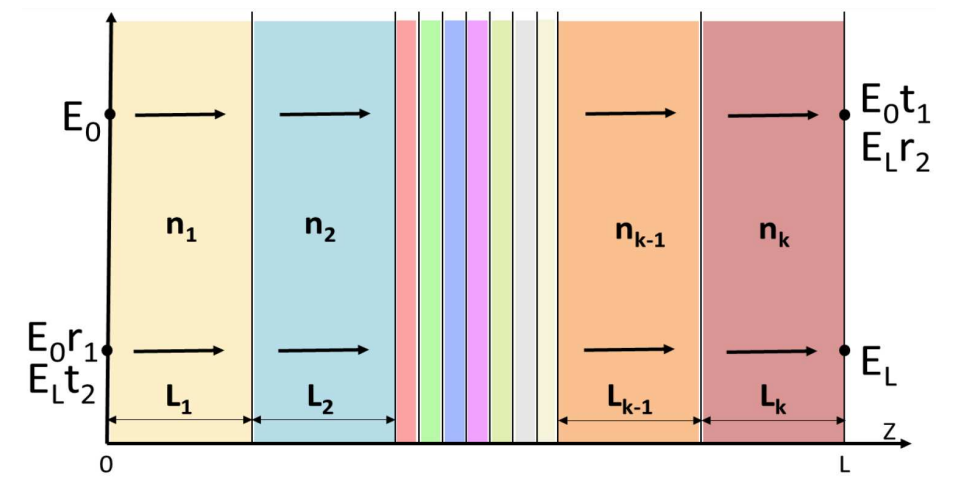 Secondary Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field in Inhomogeneous Structures Based on Formalism of Scattering MatrixA.V. Belonovskii, K.M. Morozov, K.A. Ivanov , and 1 more authorActa Physica Polonica A, Oct 2019
Secondary Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field in Inhomogeneous Structures Based on Formalism of Scattering MatrixA.V. Belonovskii, K.M. Morozov, K.A. Ivanov , and 1 more authorActa Physica Polonica A, Oct 2019We show the procedure for the secondary quantization of the electromagnetic field in an inhomogeneous medium, based on the formalism of the scattering matrix. We demonstrate the electromagnetic field profiles, which are obtained as a result of applying the scattering matrix formalism and prove their orthogonality. Finally, we derive the Hamiltonian of the system. The obtained procedure allows us to use more complete representation of quantum theory in a layered medium to describe various effects in layered structures.
@article{Belonovskii2019_2, title = {Secondary Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field in Inhomogeneous Structures Based on Formalism of Scattering Matrix}, volume = {136}, issn = {0587-4246}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.136.649}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.12693/aphyspola.136.649}, number = {4}, journal = {Acta Physica Polonica A}, publisher = {Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences}, author = {Belonovskii, A.V. and Morozov, K.M. and Ivanov, K.A. and Kaliteevski, M.A.}, year = {2019}, month = oct, pages = {649–652}, } -
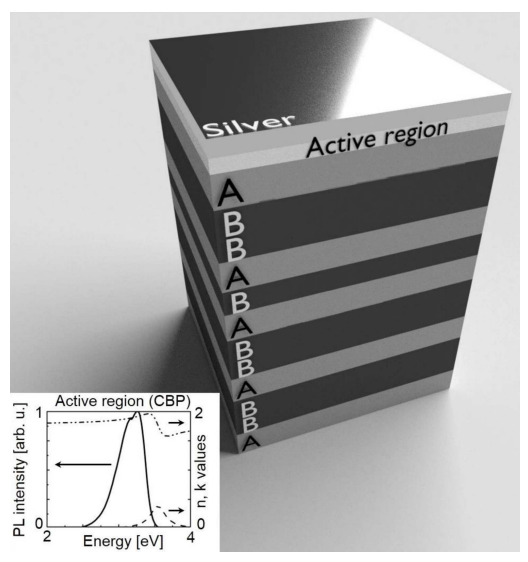 Hybrid Tamm Plasmon - Photonic Quasicrystal Cavity with an Organic Active RegionK.M. Morozov, A.V. Belonovskii, K.A. Ivanov , and 2 more authorsActa Physica Polonica A, Oct 2019
Hybrid Tamm Plasmon - Photonic Quasicrystal Cavity with an Organic Active RegionK.M. Morozov, A.V. Belonovskii, K.A. Ivanov , and 2 more authorsActa Physica Polonica A, Oct 2019Photonic quasicrystals (PQC) are a class of photonic structures, considered between ordered and fully disordered photonic systems [1, 2]. PQCs are characterized by the long-range order and lack of periodicity. Such systems have also peculiar optical properties, eg the fractal density of photonic states and the light localization determined by this—even in 1D case [3–5]. The Tamm plasmons (TP) are electromagnetic states localized at the edge between the dielectric Bragg mirror and the metal. TP modes differ from conventional surface plasmon. They have some useful advantages like the existence inside the light cone (both in TE and TM polarizations) and lower absorption losses. The use of metallic structures with photonic quasicrystal can lead to promising optical phenomena [6]. The topological properties of the TP-like state have been recently studied in a 1D photonic quasicrystal [7]. In this paper we theoretically study the hybrid Tamm plasmon—photonic quasicrystal cavity with an organic small molecule active layer. Light emission enhancement properties of this system and its general optical properties are analyzed.
@article{Morozov2019_3, title = {Hybrid Tamm Plasmon - Photonic Quasicrystal Cavity with an Organic Active Region}, volume = {136}, issn = {0587-4246}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.136.653}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {10.12693/aphyspola.136.653}, number = {4}, journal = {Acta Physica Polonica A}, publisher = {Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences}, author = {Morozov, K.M. and Belonovskii, A.V. and Ivanov, K.A. and Girshova, E.I. and Kaliteevski, M.A.}, year = {2019}, month = oct, pages = {653–656}, }
2015
-
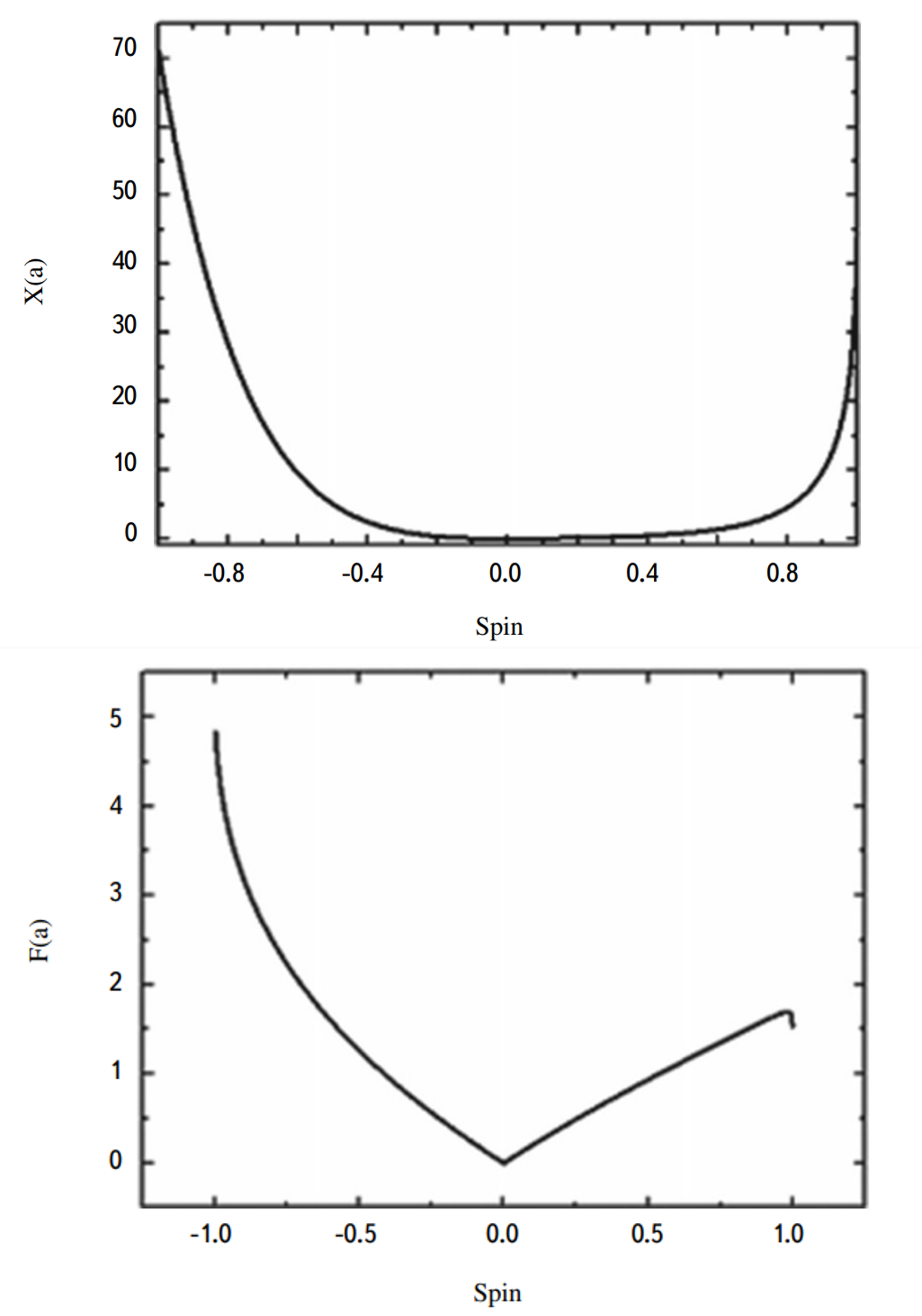 Determination of the Magnitude of the Spins of Supermassive Black Holes and the Magnetic Fields in Active Galactic NucleiA. G. Mikhailov, Y. N. Gnedin, and A. V. BelonovskyAstrophysics, Oct 2015
Determination of the Magnitude of the Spins of Supermassive Black Holes and the Magnetic Fields in Active Galactic NucleiA. G. Mikhailov, Y. N. Gnedin, and A. V. BelonovskyAstrophysics, Oct 2015Limits on the value of the spins of supermassive black holes (SMBH) in Seyfert-type active galactic nuclei (AGN) are calculated using two hybrid models for the generation of relativistic jets: the Meier model and a model of tandem Blandford-Znajek and Blandford-Payne processes. A comparison of our calculations with limits on the spin obtained by x-ray reflection spectroscopy shows that they are in good agreement for the tandem model. This shows that the magnetic field pressure is roughly equal to the radiation pressure in the accretion disk in the region of the last stable orbit. The magnitudes of the magnetic fields at the radii of the last stable orbit in the accretion disk and the event horizon of a supermassive black hole are also determined for objects in a list of 28 radio quasars. The important result is that the magnetic energy density near the radius of the event horizon turns out to be significantly higher than the energy density of the accretion gas. This may indicate the existence of a mechanism for amplification of the magnetic field near the event horizon of black holes located in the center of powerful radio quasars.
@article{Mikhailov2015, author = {Mikhailov, A. G. and Gnedin, Y. N. and Belonovsky, A. V.}, title = {Determination of the Magnitude of the Spins of Supermassive Black Holes and the Magnetic Fields in Active Galactic Nuclei}, journal = {Astrophysics}, year = {2015}, volume = {58}, number = {2}, pages = {157--167}, doi = {10.1007/s10511-015-9372-y}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-015-9372-y}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {UeHWp8X0CEIC}, issn = {1573-8191}, }
